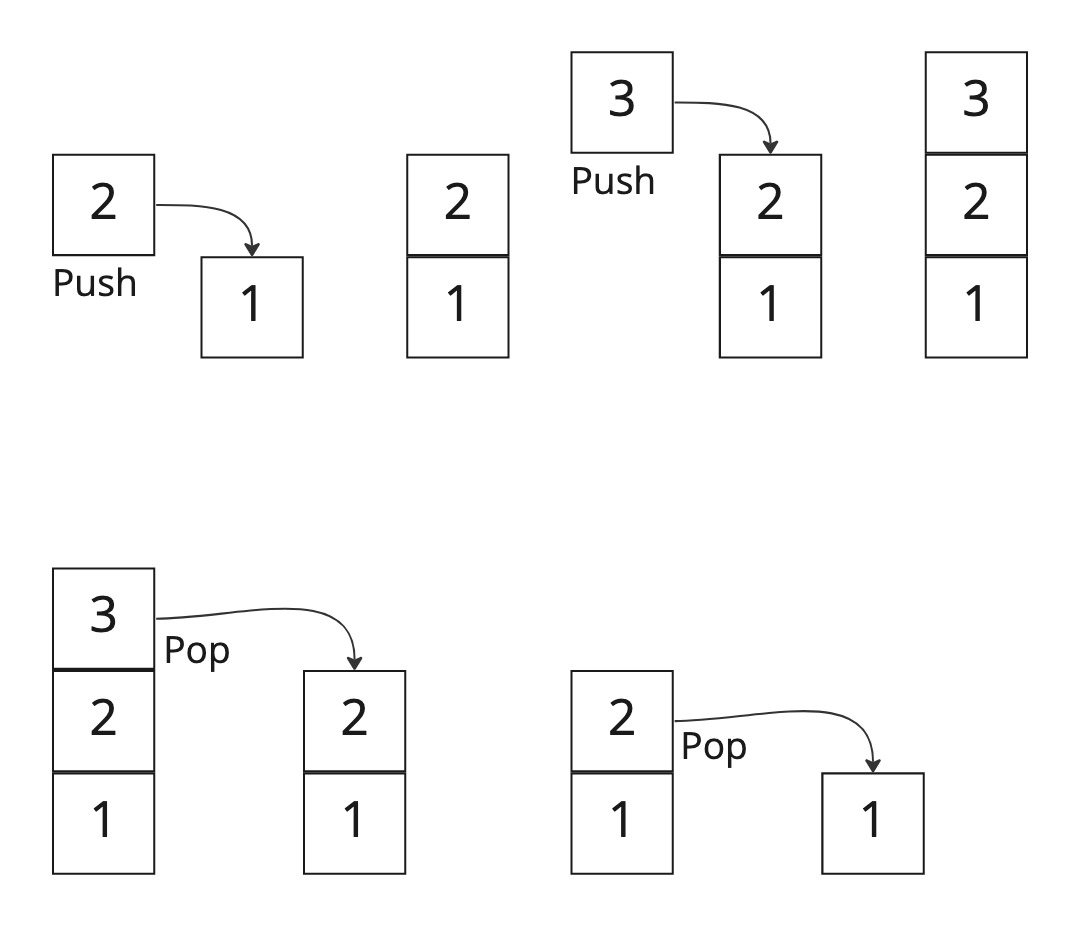
In computer science, a stack is a famous abstract data type that provides certain operations on a collection of elements. Stacks have a long history, dating back to the very first computer programs and were first documented in 1946.
While you may never need to build a stack yourself, you probably interact with one in your everyday programming in the form of a call stack, so it seems like an important concept to learn about.
Building stacks also provides an opportunity to practise our baby steps in test driven development.
For this kata, build a stack that supports these operations:
- Push - Add an element to the top of the stack
- Pop - Remove an element from the top of the stack, returning it
- Empty check - Check if the stack is empty or not
- Size - Count of the elements in the stack
- Peek - Check the top of the stack without popping
Whilst building out these operations, think about the simplest way possible first. Don't go for what you think might be the final implementation right away.
Here are some more important details to consider while building your stack. You could even think of them as iterative requirements along with your operations:
- Handle overflows when too many elements are pushed to the stack
- Handle underflows when too many elements are popped off the stack
- Handle underflows when there are no elements to peek on the stack
- Handle attempts to create a stack with an invalid capacity (negative numbers) You may recognise one of these requirements as the origin of the famous phrase “Stack Overflow”, which also serves as the name of a certain website you probably look at everyday.
After you have completed building your stack and if you want to go a bit further, try the following.
Your stack currently has protection for a capacity of 0. This is also known as a 'null stack' and a stack with more than 0 is known as a 'bounded stack'. Do you really need all that other code if you receive the request to create a null stack?
There are ways in programming to provide fixed behaviour for known situations. For example, you know for a null stack it will always be empty, always overflow when a push is attempted, and always underflow when a pop is attempted.
If the language you are using supports polymorphism, come up with a way to update the creation of a stack, so that it creates a null or bounded stack based on the requested capacity. Then you can add only the code you need to each situation. Your tests should remain the same, but the underlying behaviour has changed.
Configuración básica para empezar a hacer una kata o aprender a hacer tests en los siguientes lenguajes:
- PHP y PHPUnit
- Javascript con Jest
- Typescript con Deno
- Java, Junit y Mockito
- Scala, Munit y Scalacheck
- Kotlin, JUnit5 y MockK
- C#, xUnit (con FluentAsertion) y NSubstitute (para mock)
- Instalar composer
curl -sS https://getcomposer.org/installer | php composer install(estando en la carpeta php)./vendor/bin/phpunit
- Instalar Node
npm install(Estando en la carpeta javascript)npm test
- Instalar Deno
deno test(Estando en la carpeta typescript)
- Instalar las dependencias y tests con Maven [mvn test]
- Ejecutar los tests con el IDE
sbt(en la carpeta scala)~testpara ejecutar los test en hot reload
- Munit
- Scalacheck para testing basado en propiedades
- Instalar SDKMan
sdk install java 11.0.12-openinstala OpenJDKsdk install sbtuna vez instalado SDKMan
- Descargar Visual Studio Code
- Instalar para VS Code Metals
- Por consola: Puedes instalar dependencias y lanzar los tests con
gradlew test - Usando IDE: Simplemente abre el proyecto desde el raiz de la plantilla Kotlin
- Instalar Microsoft Visual Studio Community 2022
- Abre el proyecto y se descargaran automáticamente los paquetes Nuguet necesarios
- Instalar python 3.x
- Una vez descargado el código fuente dentro de la carpeta */python/ creamos un virtual enviroment:
python3 -m venv env- Activamos en virtual environment:
- windows:
.\env\Scripts\activate.bat - linux/mac:
source env/bin/activate
pytestpara ejecutar los tests.