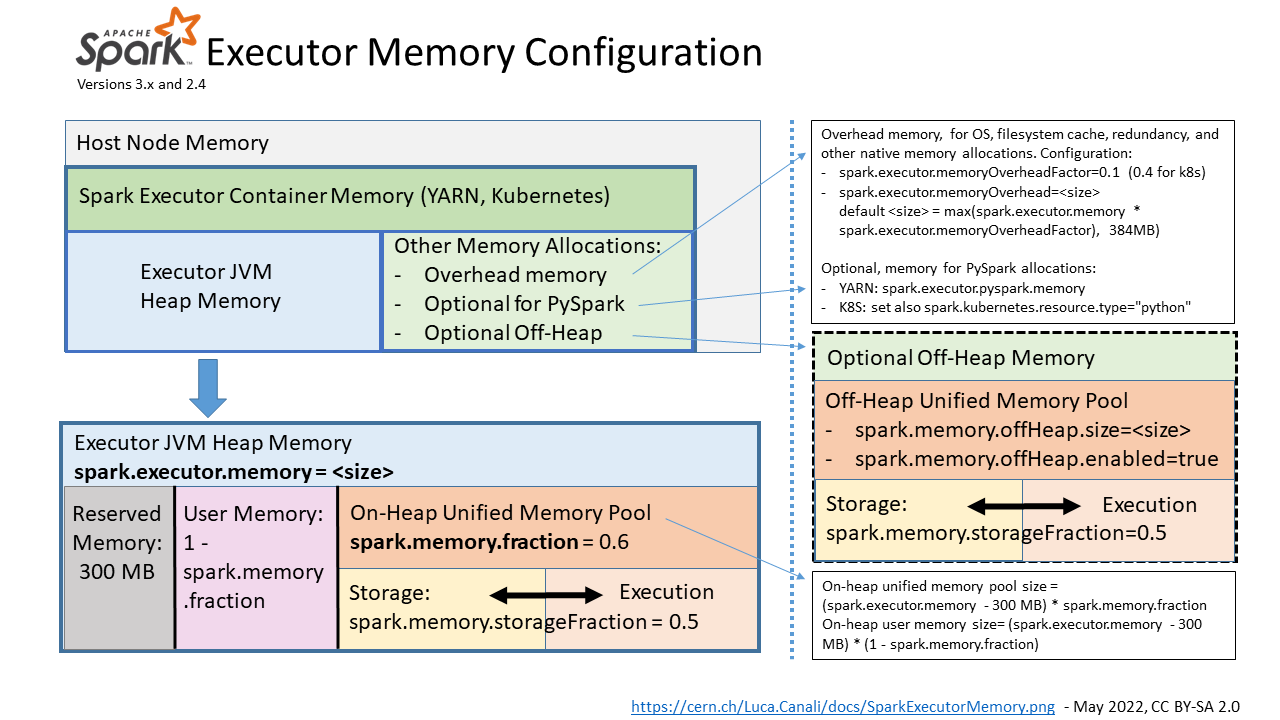
- The main configuration parameter used to request the allocation of executor memory is spark.executor.memory.
- Spark running on YARN, Kubernetes or Mesos, adds to that a memory overhead to cover for additional memory usage (OS, redundancy, filesystem cache, off-heap allocations, etc), which is calculated as memory_overhead_factor * spark.executor.memory (with a minimum of 384 MB). The overhead factor is 0.1 (10%), it can be configured when running on Kubernetes (only) using spark.kubernetes.memoryOverheadFactor.
- When using PySpark additional memory can be allocated using spark.executor.pyspark.memory.
- Additional memory for off-heap allocation is configured using spark.memory.offHeap.size= and spark.memory.offHeap.enabled=true. This works on YARN, for K8S, see SPARK-32661.
- Note also parameters for driver memory allocation: spark.driver.memory and spark.driver.memoryOverhead.
- Note: this covers recent versions of Spark at the time of this writing, notably Spark 3.0 and 2.4. See also Spark documentation
Figure 1: Pictorial representation of the memory areas allocated and used by Spark executors and the main parameters for their configuration.
- Image in png format: SparkExecutorMemory.png
- Image source, in powerpoint format: SparkExecutorMemory.pptx
Spark tasks allocate memory for execution and storage from the JVM heap of the executors using a unified memory pool managed by the Spark memory management system. Unified memory occupies by default 60% of the JVM heap: 0.6 * (spark.executor.memory - 300 MB). The factor 0.6 (60%) is the default value of the configuration parameter spark.memory.fraction. 300MB is a hard-coded value of "reserved memory". The rest of the memory is used for user data structures, internal metadata in Spark, and safeguarding against OOM errors. Spark will manage execution and storage memory from the unified memory pool. Additional structure is exposed with the configuration parameter spark.memory.storageFraction (default is 0.5), which guarantees that the stored blocks will not be evicted from the unified memory by execution below the specified threshold. The unified memory pool can optionally be allocated using off-heap memory, the relevant configuration parameters are: spark.memory.offHeap.size and spark.memory.offHeap.enabled.
The first key configuration to get right is spark.executor.memory. Monitoring data can help you understand if you need to increase the memory allocated to Spark executors and or if you are already allocating plenty of memory and can consider reducing the memory footprint. There are other memory-related configuration parameters that may need some adjustments for specific workloads: this can be analyzed and tested using memory monitoring data. In particular, increasing spark.memory.fraction (default is 0.6) may be useful when deploying large Java heap, as there is a chance that you will not need to set aside 40% of the JVM heap for user memory. With similar reasoning, when using large Java heap allocation, manually setting spark.executor.memoryOverhead to a value lower than the default (0.1 * spark.executor.memory) can be tested.